Certification, certified and certificates are all terms that you’ll find bandied round by jewelers, people talking about diamond and anyone that has done any research at all around diamonds. It’s even sometimes included as the 5th C of diamonds.
So what does it really mean, how important is it and how do you make sure that you get the best ‘certificate’?
What is certification?
Certification is the process of assessing and grading a diamond against predetermined characteristics – the 4Cs of cut, color clarity and carat. Basically putting them through the NFL Scouting combine to see how they measure up.
This process is conducted by independent labs who then issue a ‘grading report’ detailing the 4Cs, which is then used by retailers to work out the price of a stone.
There are many labs across the world that conduct grading reports, but they aren’t all equal. Some have super strict standards, while others are more lax. This is important because you want to make sure that you are getting what you pay for. But more on that later.
Watch out: Grading labs don’t actually ever use the term ‘certificate’. It’s the commonly used term in the jewelry industry, but you’ll never see it written on a report. Instead they will talk about a ‘grading report’ or similar. In this article I’m going to continue to use ‘certificate’ because it is the most commonly used term and it applies across all of the grading labs.
Why is certification so important?
Certification is hugely important for four reasons:
1. Verify it’s the real deal
The first is to make sure that what you are getting is the real deal – a natural diamond and not a lab-grown ‘cultured’ diamond. This is getting more important as advances in the technology for producing lab-grown diamonds means that they can be incredibly difficult to distinguish from the real thing.
In 2011, a large batch of synthetic diamonds entered the diamond supply chain when a dealer, who believed them to be real, sold them on to jewelers. They were so convincing that when examined under a microscope by an experienced jeweler, there was no indication that they weren’t natural diamonds.
The switcheroo only came to light when one of the stones from the batch was examined by a grading lab, who used high-tech photoluminescence equipment to show that they had been grown artificially.
2. Highlight treatments
The second reason that certification is important is because it will verify whether a stone has been treated in any way to improve its appearance. Treatments can be applied to diamonds to improve the colour or clarity of a diamond. It’s very difficult to tell whether stones have had treatment applied to them, but stones that have been subject to them are worth considerably less than natural stones.
Much like the dude who divorced his wife when he found out that she had had a ton of plastic surgery before they met, but then passed her less-than-awesome genes on to their kids, you want to make sure that you are getting the real, and naturally beautiful, deal.
However, this consistency of grading only applies within individual organisations. Although the same terminology around the 4Cs is used by different labs, they definitely don’t grade diamonds in the same way, as we’ll see.
3. Gives you confidence
Knowing that the diamond that you are considering has been assessed by an expert should give you great confidence in your purchase. It is the reason why you can safely buy online – any diamond that you are looking at has been graded by someone with years of experience to help you make a considered choice. Rather than being subject to sales spiel or dazzled by the bright lights of a bricks and mortar jewelry store, comparing the grading reports means that you can make an informed decision to get the perfect diamond for your engagement ring at the best possible price.
A Diamond Certificate or Diamond Grading Report is a statement, issued by an independent Gemological Laboratory. At the time of evaluation, the diamond in question has been examined, measured, and scrutinized by experienced Diamond Graders, using various gemological instruments, and determined to contain the characteristics as stated in the Certificate or Report.
In other words, a diamond certificate can be accurately described as the blueprint of a diamond. This Certificate or Report includes an analysis of the diamond's characteristics in an easy to understand format. Generally, a certificate or report covers the following characteristics of a diamond along with the laboratory and certificate details:
- Name of the Laboratory
- Certificate Number
- Shape and Cutting Style
- Measurements of the Diamond's diameter
- Carat Weight
- Color Grade
- Clarity Grade
- Cut Grade
- Finish, Polish & Symmetry
- Fluorescence
- Comments
- Plotted diagram of the diamond that shows the imperfections.
- Key to Symbols that help identify characteristics marked in the plot.
- Security Features for the certificate
- Graphical image of Diamond Structure
- Information about Diamond's Depth, Table, Girdles, Culet and Facets etc.
This certificate doesn't state the monetary value of a diamond.
There are many laboratories available throughout the world for diamond certification but the below mentioned laboratories are considered the most respected ones in the industry, for their consistency and unbiased diamond grading systems. Securing a certificate will provide you much-needed peace of mind knowing that you are getting your money's worth. Here are some reasons to buy a diamond along with its certificate:
A diamond certificate gives you the exact details of the stone and on the basis of this information you will be able to do some comparison-shopping before doing the actual purchase. A diamond certificate allows you to purchase on the basis of a stone's characteristics.
If you resell the diamond along with its certificate, you will get better price for the diamond. To get insurance for your diamond, you also need to produce a diamond certificate.
GIA - Gemological Institute of America:
The Gemological Institute of America was established in 1931 in Los Angeles. The GIA created and introduced the international grading system. Headquarters are still located in Los Angeles.
The GIA, or Gemological Institute of America, is focused on teaching people about Jewelry and gems. It's non-profit and mostly research based. All types of different gemstones are graded through the GIA, and Diamonds are a part of that. Gemologists can be trained through this organization, as well, and there's a lot of support offered to the diamond industry. Currently, the GIA is top rated when it comes to the certifications and verifications of Diamonds throughout the Jewelry and gemstone industries. This is due to their strict grading standards and international acceptance.
If you buy a diamond with a GIA rating and grading, you know what you're getting and that you're receiving a quality stone. The GIA is the organization that came up with the current grading standards that are accepted industry wide, so they are truly the industry leader in diamond grading. If you have a GIA graded diamond, you have a stone you can feel good about and have confidence in based on the quality of the diamond and the value that has been placed on it. While there are a number of other certification labs, the gold standard for grading Diamonds is generally understood to be the GIA.
TYPES OF CERTIFICATES ISSUED BY THE GIA
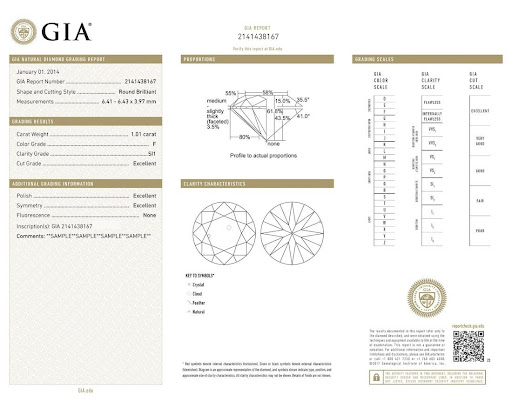
- GIA Diamond Grading Report: Documents the carat weight, clarity and color grades of a diamond, as well as its exact measurements, and in the case of round brilliant cuts, a cut grade. See above for an example.
- GIA Diamond Dossier: Issued for diamonds weighing less than 1.00 carat.
- GIA Colored Diamond Identification & Origin Report: Describes color grade and color origin (i.e. natural or treated) of colored diamonds of any size. A full color image may also be requested as an additional service.
Full Grading Report
The full grading report includes the dimensions of the stone, the grading of the 4 Cs and any other identifying information in the left hand column.
The center column includes the proportions of the diamond and a plot of all of the ‘clarity characteristics’ ie. the flaws on the stone.
Lastly, the right hand column includes a key to explain the certificate.
Dossier
A ‘dossier’ is often used for smaller stones. It’s less expensive than the full report for a lab to produce, so it can make more sense to not incur the cost of the producing a full grading report for a less valuable stone.
Although the dossier still includes the dimensions of the stone, the grading of the 4 Cs and any other identifying information and a diagram of the proportions of the diamond, it doesn’t include a plot of the diamond’s inclusions.
THE DIAMOND HIGH COUNCIL - HOGE RAAD VOOR DIAMANTE (HRD)
The Diamond High Council is the officially recognized representative of the Belgium diamond trade and industry. HRD headquarters are located in Antwerp, Belgium, in the World Diamond Center.
Founded in 1976 to meet the growing demand for reliable diamond certificates, the HRD is a non-profit organisation at the service of the Belgian diamond trade and industry. Since its foundation in 1976, the HRD Certificates Laboratory has expanded into one of the largest diamond certification labs in the world and maintains an excellent reputation for quality and objectivity.
Each diamond is examined independently by several experts withvery sophisticated machinery, such as spectophotometres, Dia-Mention systems, and cathode luminescence apparatus to ensure a high level of reliability.
TYPES OF CERTIFICATES ISSUED BY THE HRD
HRD Diamond Certificate: A certificate detailing the shape , measurements, carat weight, clarity, fluorescence, color and finish grades of a diamond as well as a plotted diagram. See above for an example.
- HRD Diamond Identification Report: A simpler version of the diamond certificate detailing the same characteristics as above but without a plotted diagram.
- HRD Diamond Color Certificate: A certificate outlining the color description, origin and luminescence of fancy colored stones.
- The American Gem Society Laboratories (AGSL)
The American Gem Society Laboratories (AGSL) was established in 1934 in Las Vegas, Nevada by Robert M. Shipley, who also established the GIA.
It is standard practice in the diamond industry, to ask for a diamond's certificate or grading report from the jeweler before the purchase of it.
The AGS uses a different scale than the GIA for clarity and color – possibly a more logical scale based on 1-10 for color and clarity.
You can compare the AGS’s clarity scale to the GIA’s:
And the AGS’s color scale is:
However, it’s much more likely that you’ll come across the GIA’s scale for grading diamonds than the AGS’s.
The GIA and the AGS are the two most reputable grading labs and the two that I would recommend. They have the best interests of the consumer in mind, rather than providing overly-generous grading reports which will increase a jeweler’s profits at the expense of the consumer.
TYPES OF CERTIFICATES ISSUED BY THE AGS
AGS Diamond Quality Document: A document evaluating the color, clarity, carat weight, and cut of a diamond, including a detailed diagram plotting the diamond's proportions and illustrating any present inclusions. See above for an example.
- AGS Diamond Quality Report: A report detailing the cut, color, clarity, and carat weight of diamonds in both AGS and GIA terminology.
THE INTERNATIONAL GEMOLOGICAL INSTITUTE (IGI)
One of the leading gemological institutions in the world, the IGI was established in 1975 in Antwerp, with a sister laboratory in New York, and has since become the largest independent gem certification and appraisal institute renowned for its quality services, extensive experience and expertise. What originally began with just 3 staff members has expanded to over 250 professionals dedicated to a remarkable standard of excellence in Antwerp, New York, Bangkok, Mumbai and Tokyo.
The IGI issues more than 400,000 reports per year. Thousands of jewellers, retail stores, insurance companies, internet sales organisations, catalogue companies, accounting and securities firms and consumers rely on the IGI reports.
International Gemological Information, a division of IGI, was established in New York in 1981, as a source for unbiased appraisals of gems and jewellery. Like its parent company, IGI Information is totally independent of all commercial sales organisations and does not trade in diamonds or precious stones. Therefore IGI Information is able to provide objective and accurate appraisals and identification reports, alongside appraisal updates and estimates in case of damage.
TYPES OF CERTIFICATES ISSUED BY THE IGI
- IGI Diamond Report: A detailed analysis of the stone's characteristics, including carat weight, color, clarity, polish and symmetry, and proportions. A diamond diagram with plotted clarity characteristics is also included. See above for an example.
- IGI Diamond ID: A passport-sized document that contains the same detailed information as the Diamond Report, without the plotted diagram. This report is also available in a more compact credit card size.
- IGI Hearts and Arrows Diamond Report: A report rating optical symmetry.
THE EUROPEAN GEMOLOGICAL LABORATORY (EGL)
Founded over thirty years ago in Belgium, the EGL is committed to protecting the integrity of the jewellery trade and fuelling public interest through applied science, education, innovation, and exceptional services. The EGL has an international presence with laboratories based in Antwerp (1973), Johannesburg (1980), London (1981), Paris (1981), Tel Aviv (1982), Istanbul (1990), Seoul (1990), Mumbai (2003) and Cape Town (2007). It is sometimes referred to therefore as 'GL Worldwide' or 'EGL International': The same standards apply to all these labs, but differ from EGL USA.
The EGL is accredited with introducing new approaches to diamond grading, the practice of certifying diamonds measuring less than 1.00 carat in weight, and establishing the SI3 diamond clarity designation. The organisation is also recognised for conducting advanced research with renowned physicists, geologists, and mineralogists.
TYPES OF CERTIFICATES ISSUED BY EGL INTERNATIONAL
- EGL Diamond Certificate Report: A certificate evaluating the color, clarity, carat weight, and cut of a diamond, including a detailed diagram plotting the diamond's proportions and illustrating any present inclusions. See above for an example.
- EGL Mini Certificate: A more compact version of the Diamond Certificate Report.
- EGL "CertiCard": The most compact of EGL certificates, this details the information as in other EGL certificates on a credit card type of document.
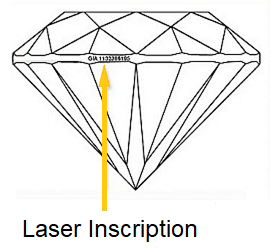
Laser engraving of the diamond
Laser engraving of your diamond is a guarantee. It allows you to identify your stone in the event of repairs or loss. You can choose to engrave your diamond’s certificate number or a personal message. Check with your insurance company. With this additional security, you should be able to obtain a discount. Engraving is located on the girdle (circumference) of the diamond and is visible using magnifying glass that enlarges 20 times :